Sole Performance - Concept
UX | UI
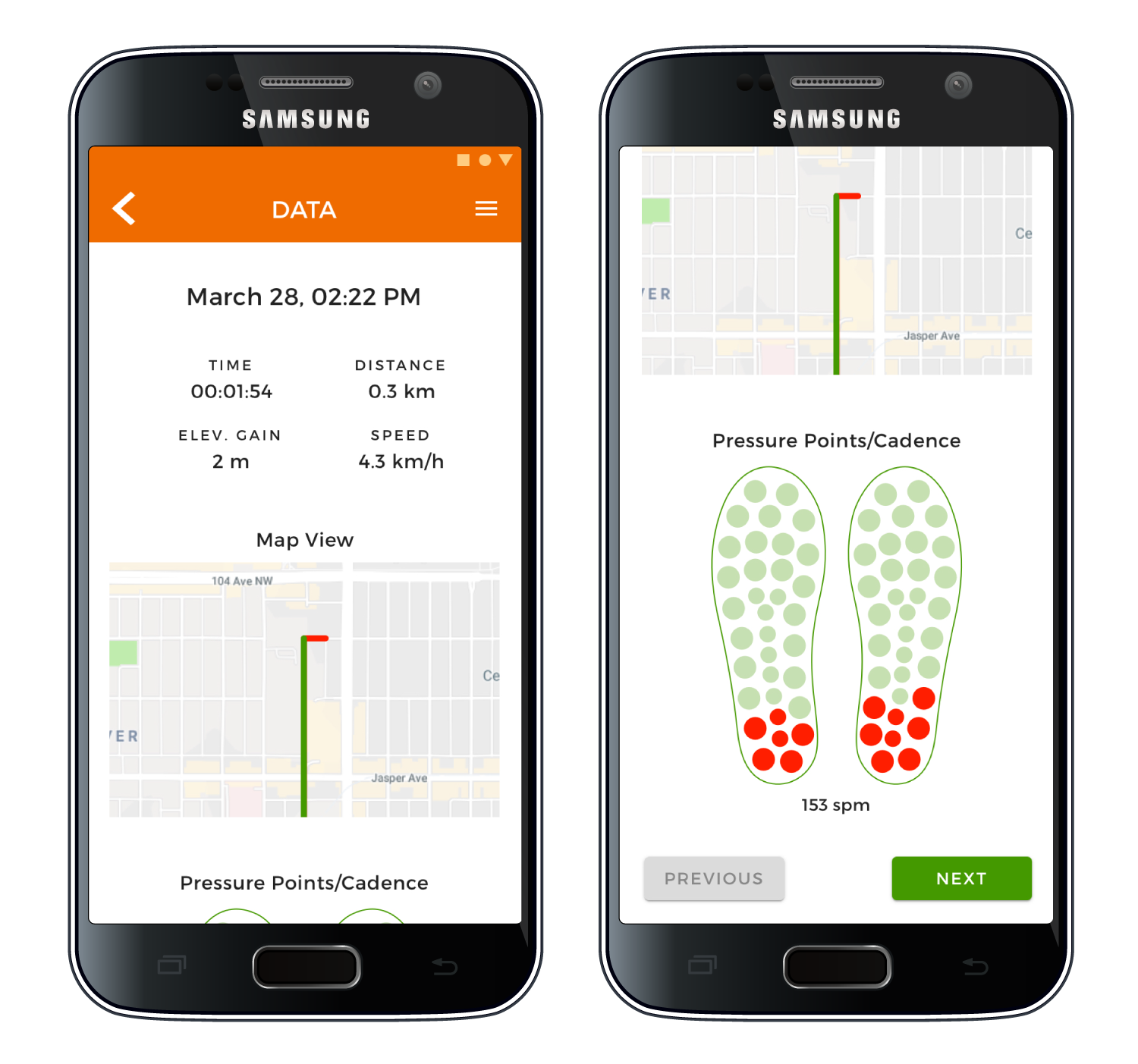
Sole Performance is a smartphone/smartwatch app and insole paired system created to help runners of all levels improve performance and reduce risks of injury. The insoles contain pressure transducers designed to measure cadence and impact area on the feet.
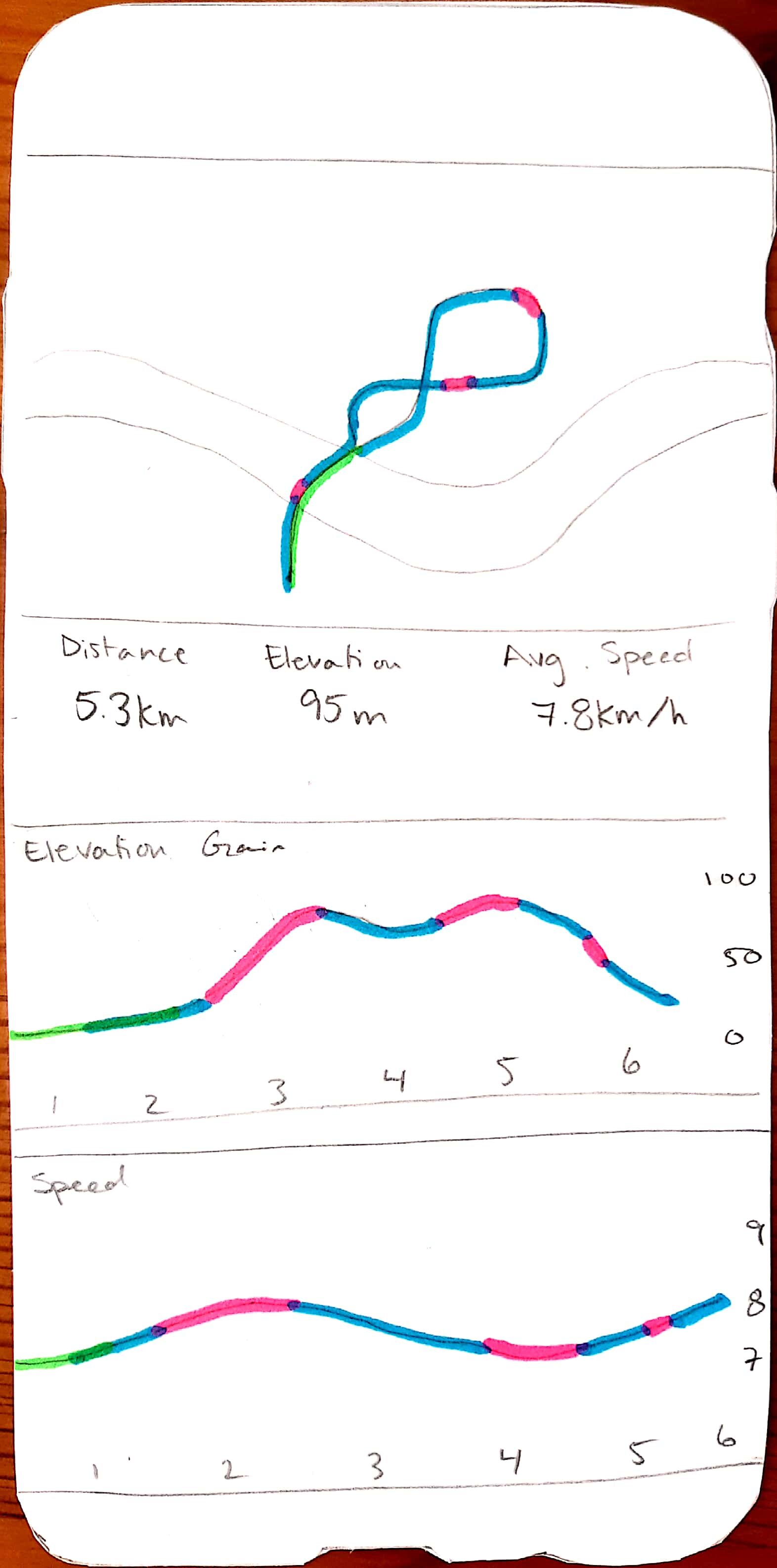
The information from the insoles is sent in real-time to the app via bluetooth, allowing the app to notify users through vibration or sound notifications exactly when their running form is incorrect. The app is also able to detect changes in terrain, when the running starts and stops, and travel path.
Context:
Goal
The purpose of this project was to improve a user’s running technique by collecting data from an insole and transferring feedback in real-time to the user through a smartwatch.
Tools
Sketch
InVision
Team & Role
Amelie Dufresne – UX/UI Researcher & Designer
Discovery:
1. Research on existing technology
Key findings:
Data portraits shift medicine from being about treating diseases, to prevention.
Quantified-self refers to the use of technology to collect data about oneself. These technologies include smartphone apps, GPS devices, and physical activity trackers.
They allow individuals to track their activity, steps, food intake, sleep, heart rate, and mood. These trackers may help users take action to improve their health.
Some commercially available in-shoe data measurement systems have high resolutions, but can be costly and therefore are used mainly in clinical diagnostics and research purposes.
Other less expensive systems have low resolution due to a low number of sensor, reducing accuracy, resulting in the possibility of missing important details. These insoles are not necessarily affordable to the masses.
Tested insoles were deemed sufficiently accurate for quantitative analysis.
[New Scientist]. (2015, November 30). The quantified self [Video File]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8wqC6ad1V_Q
Rettner, R. (2013, August 26). What is the Quantified Self? Retrieved from https://www.livescience.com/39185-quantified-self-movement.html
Tan, A. M., Fuss, F. K., Weizman, Y. & Troynikov, O. (2015). Development of a smart insole for medical and sports purposes. Procedia Engineering, 112, 152-156.




2. Ideation
Brainstorming possible ways to integrate health improvement features to wearable devices.
3. Problem Identification
- Having proper running technique is difficult to learn without a coach.
- Improper technique is a major cause of injury for runners.
- Creating an app that connects to an insole which can identify pressure points while running would help amateur runners learn proper running technique.
User Statement
“As an amateur runner, I want to get feedback on my running technique and shoes so that I can improve performance to conserve power and reduce the risk of injury.”
4. Proto-Persona
5. Requirements
6. Sketches
Develop
1. Wireframes
Smartphone and smartwatch wireframes
2. High Fidelity Mockups
Android App
Smartwatch App
Solution:
A phone and smart device app that connects to insoles with pressure transducers that measure cadence and foot strike in real-time.
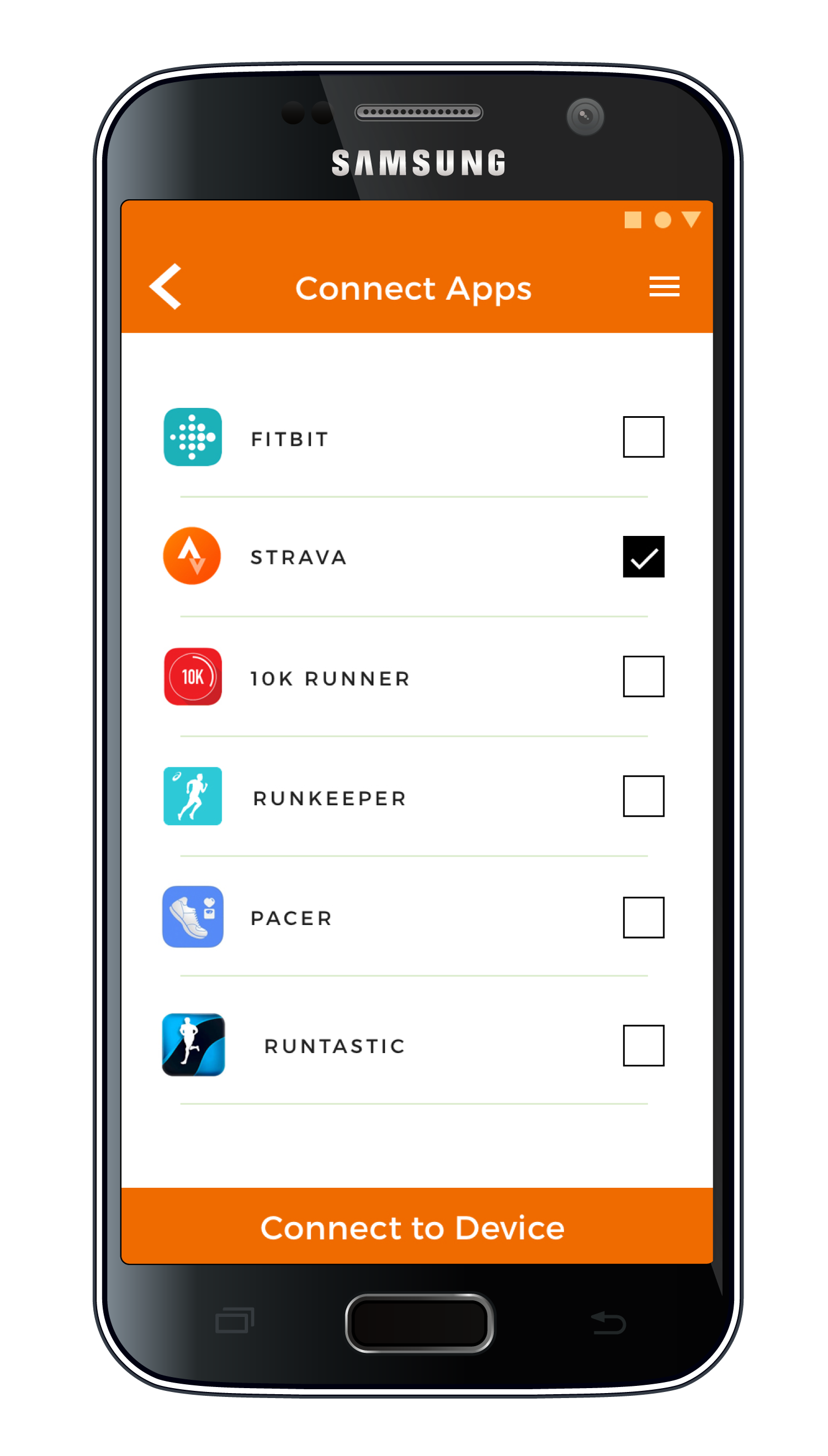
Various smart devices and apps can be connected to the app in order to share data.
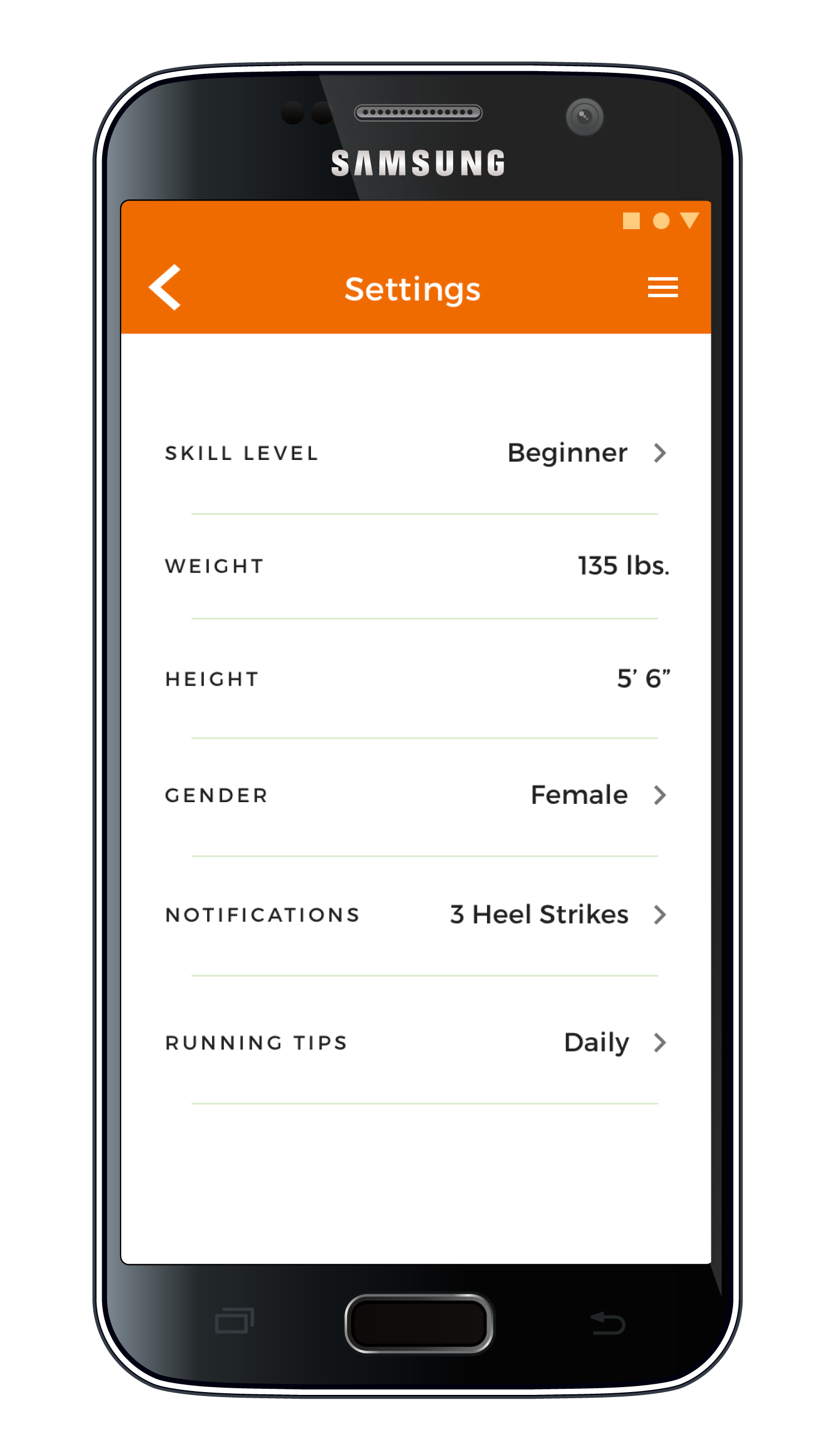
Users can adjust app settings to their body and running skill level.
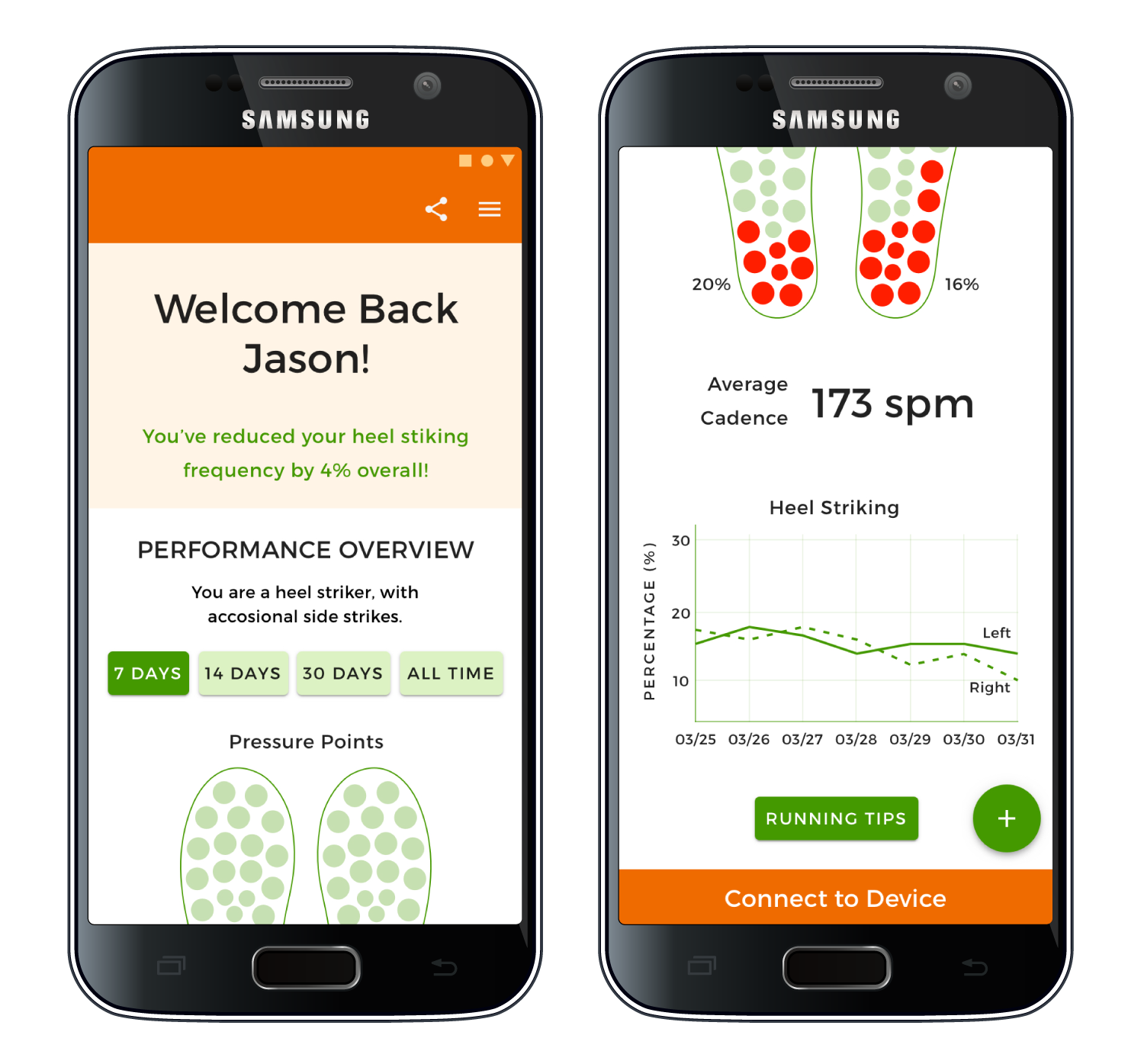
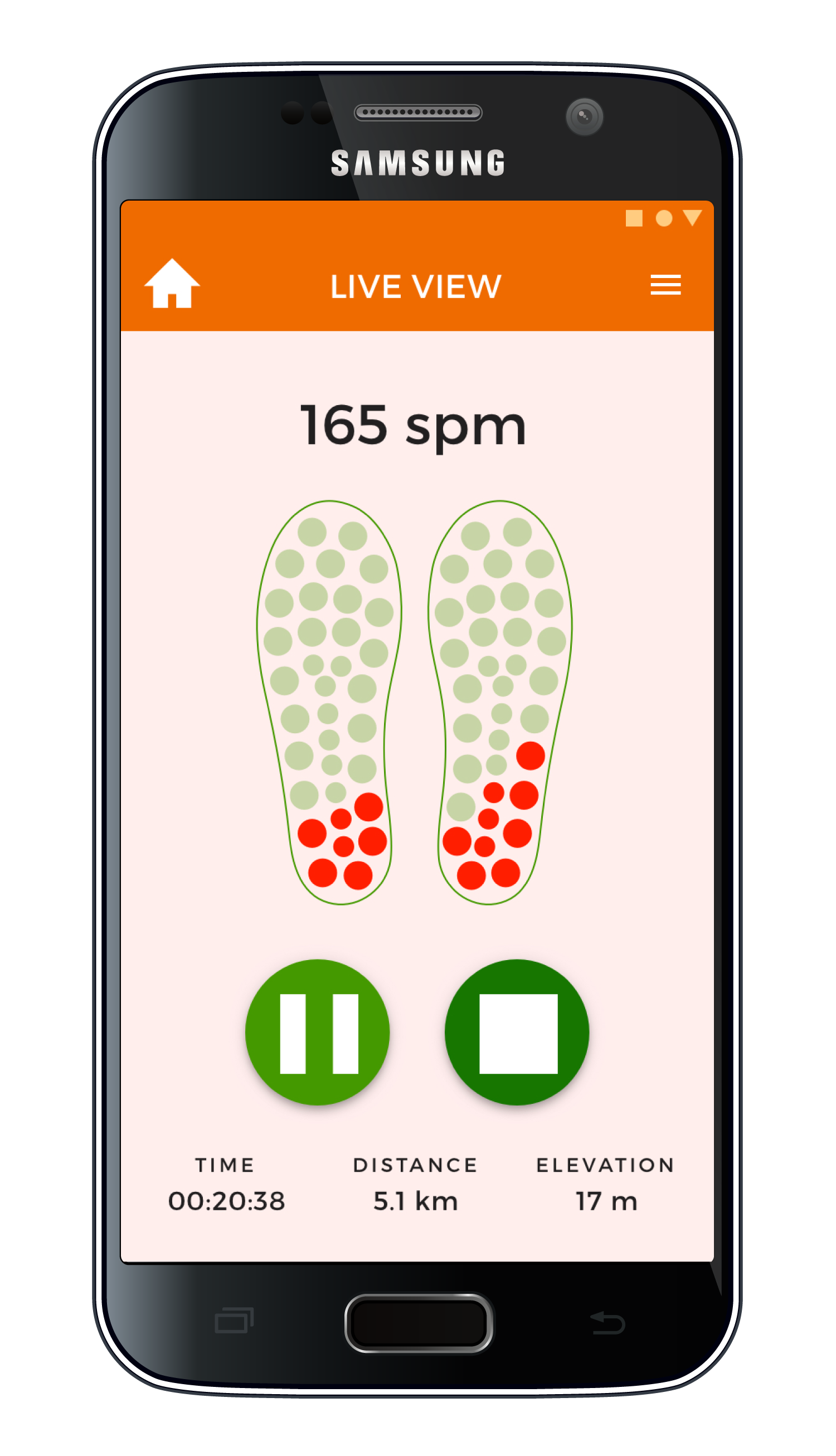
Alerts the user if running cadence or foot strike are problematic, allowing the runner to immediately adjust running form.
Running pauses and changes in terrain are automatically detected through changes in insole pressure.
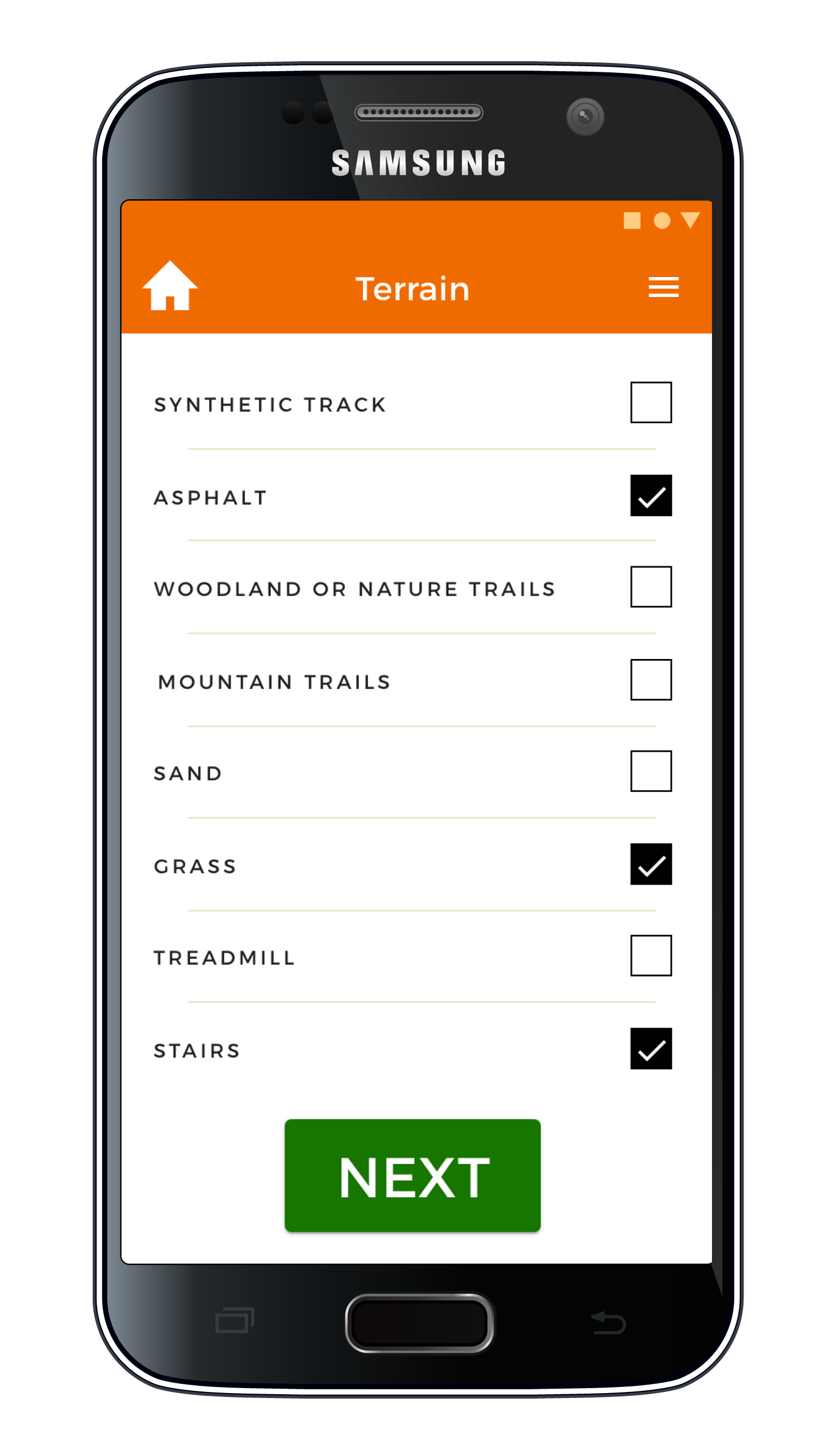
For each run, the user can select what terrain types they expect to encounter, this helps the insoles detect terrain changes.
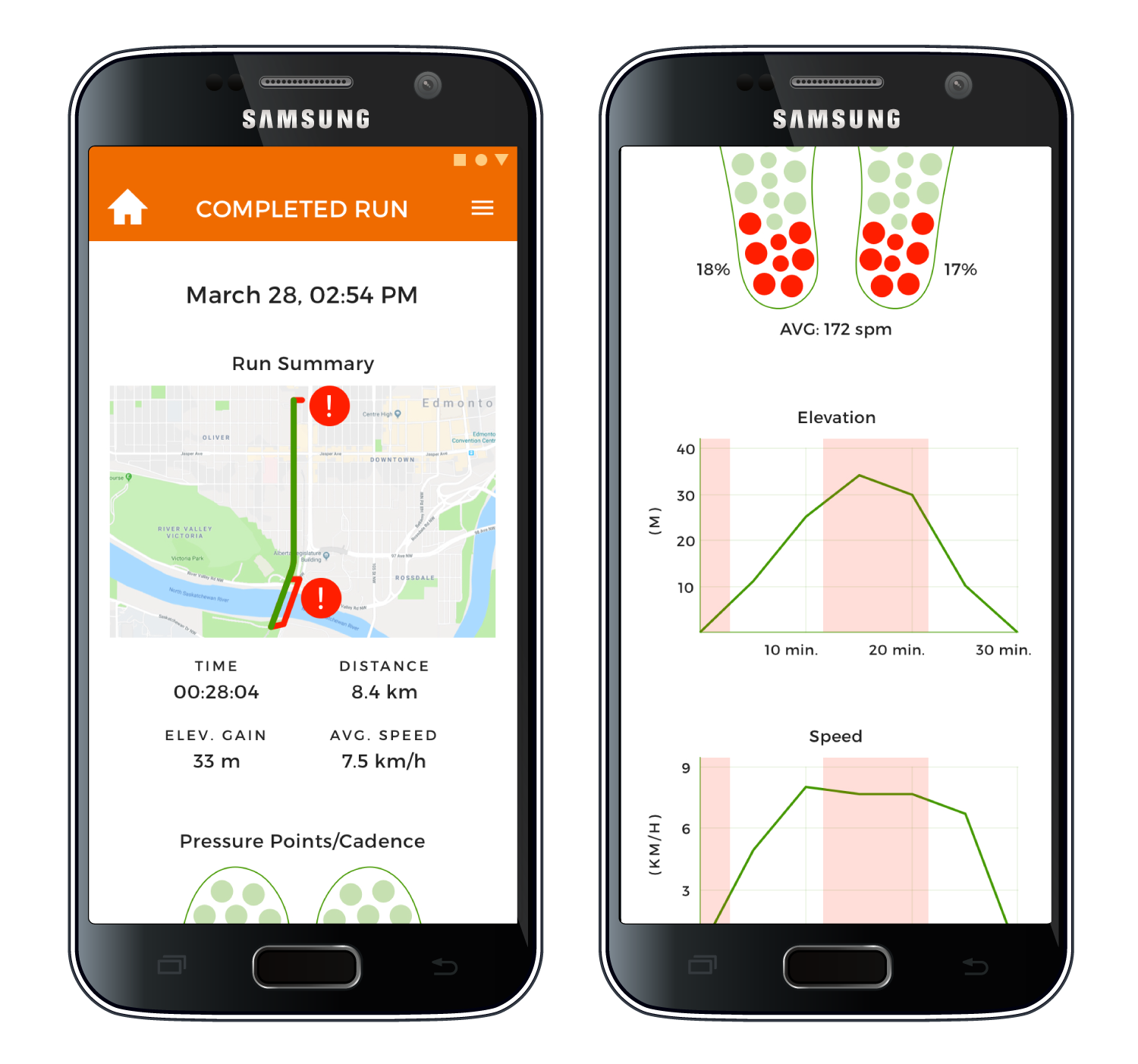
Provides a performance overview of each run and progress over time, including foot pressure points, heel striking frequency, speed, cadence, maps, and elevation.
Encouraging messages and running tips are given to the user based on their data.